Bellflower, used in folk medicine, shown to have liver protection properties
01/11/2018 / By Russel Davis
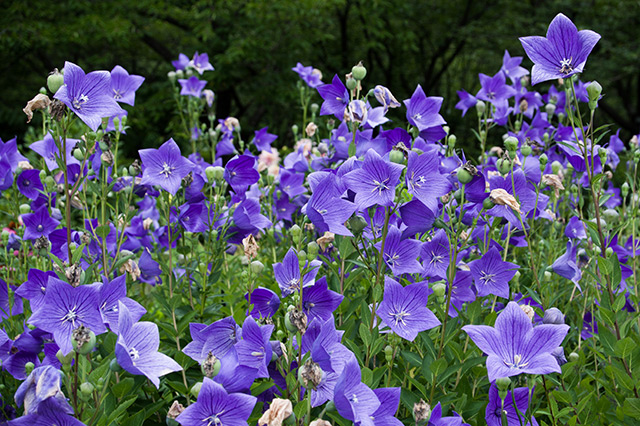

The active ingredient in the roots of Platycodon grandiflorum, more commonly known as bellflower, contain powerful properties that help protect against liver diseases, according to an animal study published in the African Journal of Traditional, Complementary and Alternative Medicines. A team of Chinese researchers examined the pharmacological activities and hepatoprotective properties of the compound Platycodin D (PD) as part of the study.
The scientists pooled data from rat models with ethanol-induced fatty liver (EFL) to determine the plant compound’s beneficial effects. The experts gave the rats 20 milligrams to 30 mg. of PD for every kilogram of body weight per day for four weeks. The research team also ran a series of assay tests on the animals’ hepatic histochemistry, liver function enzymes, and oxidative stress levels as well as antioxidant enzymes and signal path enzymes.
The researchers observed that the plasma levels of important liver disorder markers such as serum alanine transaminase and aspartate transaminase in the animal models significantly increased by 232.38 percent and 323.59 percent, respectively. However, treatment with PD help reverse these levels, the researchers reported.
“PD significantly increases hepatic antioxidant enzyme expression… improves the oxidative stress… and then improves the liver injury degree by histological evaluation. PD is an effective inhibitor of EFL,” the scientists concluded.
The experts also found that the active ingredient helped activate the signal path enzymes of Kelch-like ECH associated protein 1, nuclear factor erythroid2 and small Maf proteins in either in vitro or in vivo settings. Likewise, the results showed that the compound increased the hepatic antioxidant expressions of specific enzymes and relieved liver injury by certain degrees.
“Treatment with PD effectively protects against [alcohol-induced fatty liver] through anti-inflammatory and anti-endotoxic process, and the confirmed mechanism is that PD treatment ameliorate alcoholic-induced liver injury… In conclusion, these findings suggested that PD could be a potential candidate for the treatment of liver injury of AFL,” the researchers added.
The many other health benefits of the bellflower
An entry posted on the Naturalpedia website revealed that bellflowers help improve the respiratory system’s overall health. According to the article, the plant can be used to alleviate severe infection of the larynx and mucus accumulation in the bronchial tubes of the lungs as well as other respiratory conditions including bronchitis, hoarseness, cough and sore throat. The herbal medicine was known to relieve phlegm, wheezing and lung congestion. Bellflowers may also reduce the risk of developing lung cancer.
Aside from this, bellflowers were also touted to ease various digestive illnesses such as gastrointestinal issues, diarrhea, and dysentery as well as ulcers and other kinds of intestinal disorders. The plant can also relieve symptoms of hemorrhoids. In addition, the medicinal plant was found to fortify the immune system and help fend off fever, flu, and other infections. (Related: How to Beat and Prevent the Avian Flu and Other Influenzas.)
Bellflowers were found to prevent the onset of brain disorders and improve the central nervous system’s health as well. The plant may also relieve anuria, a condition characterized by the kidneys’ inability to produce urine. Additionally, the medicinal plant can be used to treat abscess and edema. According to the article, bellflower contains pain-relieving and anti-inflammatory properties that were touted to be at par with or better than certain medications such as aspirin.
Furthermore, the medicinal herb may promote blood cholesterol and blood sugar control. Bellflowers’ high saponin content may also mitigate the growth of carcinogenic cells and tumors. The medicinal herb was also found to possess strong analgesic, antipyretic and sedative properties.
Visit Medicine.news and be in the loop with the latest information about herbal medicine and alternative treatments.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: bellflower, flower, herb, herbal medicine, liver disease, liver health, medicinal plant